What Is A Dual-Air Brake System? Everything You Need To Know
A dual-air brake system is a vital safety feature employed in various commercial and recreational vehicles. This article delves into the comprehensive details of this braking system, exploring its components, functioning, advantages, disadvantages, and its critical role in ensuring safer and more reliable road transportation.
Table of Contents
What is a dual-air brake system?
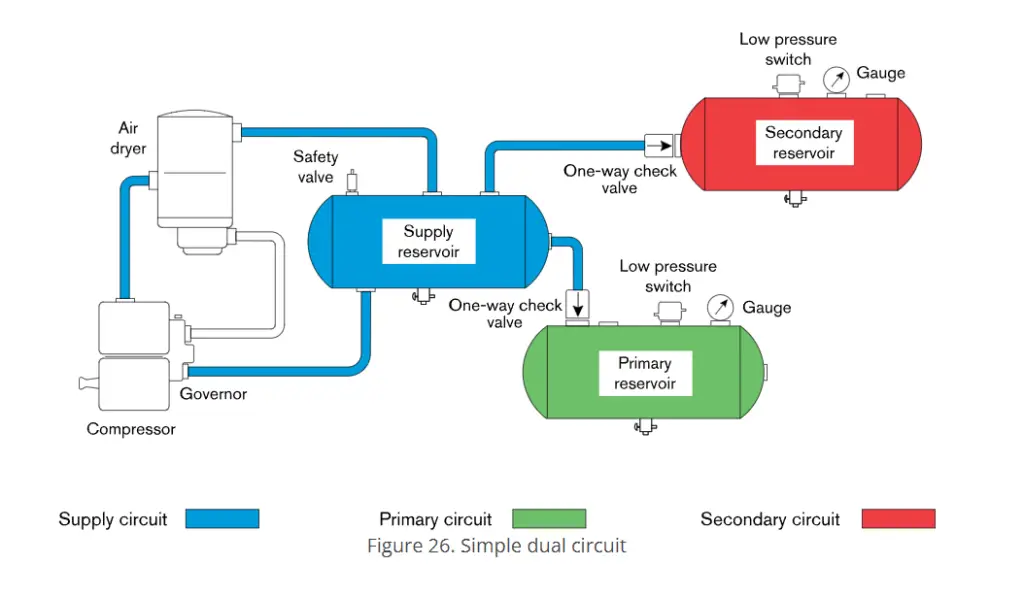
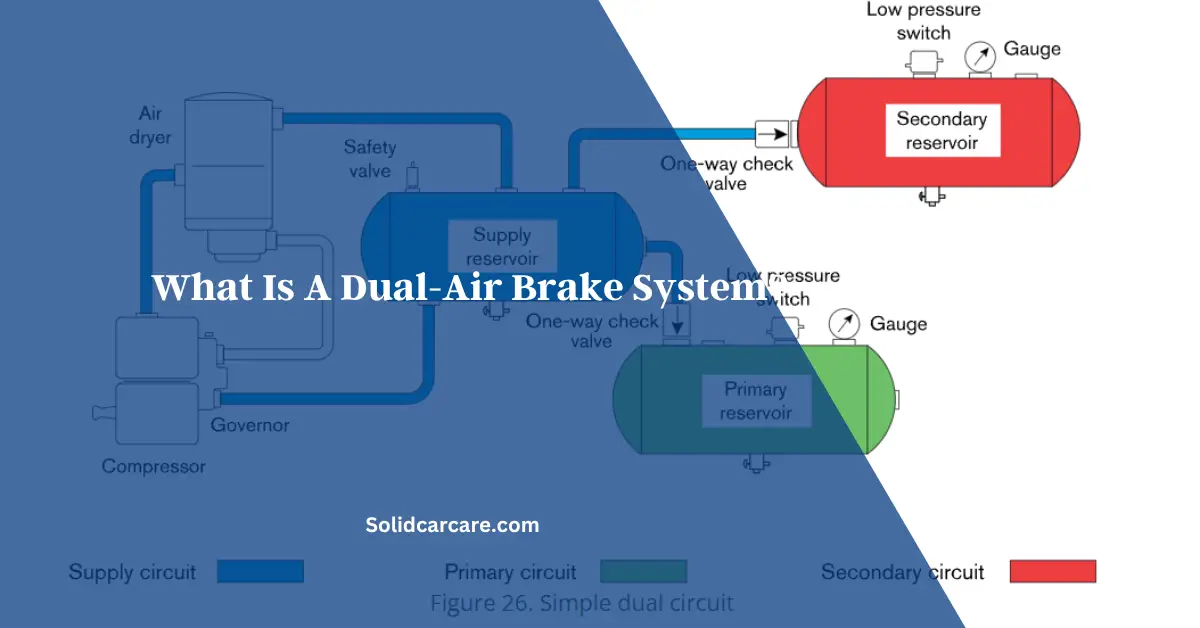
A dual air brake system is a safety feature employed in commercial and some recreational vehicles. It comprises two independent sets of components, including air reservoirs, air lines, brake chambers, a control valve, and a spring brake actuator.
One set is the primary air brake system, while the other is the secondary system. This redundancy ensures that if one system fails, the other can still operate the brakes, albeit with reduced power. This design enhances safety by preventing complete brake failure and is mandated for many commercial vehicles like trucks, buses, trailers, and school buses.
What is the purpose of using a dual brake system?
The primary purpose of using a dual brake system, also known as a dual air brake system in the context of air brakes, is to enhance safety and provide a backup mechanism in case of brake system failures. Here are the key purposes:
Redundancy and Backup
A dual brake system comprises two separate and independent brake systems within a vehicle. If one system fails due to a malfunction or loss of air pressure, the other system can still operate the brakes.
This redundancy ensures that the vehicle can come to a stop even in the event of a brake system failure, which is crucial for the safety of commercial vehicles.
Improved Safety
Using a dual brake system significantly reduces the risk of complete brake failure, which could result in accidents, particularly in heavy commercial vehicles like trucks and buses. It provides an additional layer of safety for both the driver and other road users.
Shorter Braking Distances
Dual brake systems often provide shorter braking distances than a single brake system because they can apply more braking force to the wheels. This can be especially important in emergencies where quick stopping is necessary to avoid accidents.
Enhanced Vehicle Control
Two brake systems allow the driver more options for controlling the vehicle’s speed and stopping distance. If one system is not functioning correctly, the driver can rely on the other system to help maintain control over the vehicle.
In summary, using a dual brake system aims to ensure safety, reduce the risk of brake system failure, and provide backup braking capability in case of malfunctions, ultimately enhancing the safety and control of commercial and recreational vehicles.
What is the difference between single and dual air brake systems?
The primary difference between single and dual air brake systems lies in redundancy and safety. A single air brake system has a single set of components, including air reservoirs, air lines, and brake chambers. If any component in this system fails, the entire braking capability is compromised.
In contrast, a dual air brake system consists of two independent sets of these components, offering redundancy. If one system fails, the other can still operate the brakes, albeit with reduced power.
Dual systems enhance safety, reduce the risk of brake failure, provide shorter braking distances, and offer better vehicle control, making them a critical requirement for many commercial vehicles, including trucks and buses.
Secondary Collision Brake System Malfunction: Ensuring Safety on the Road
solidcarcare.com
What are the advantages and disadvantages of a dual air brake system?
Advantages of a Dual Air Brake System
- Enhanced Safety: The primary advantage is increased safety. Dual air brake systems provide a backup if one system fails, ensuring the vehicle can still stop. This redundancy reduces the risk of accidents due to brake system failures.
- Shorter Braking Distances: Dual systems often deliver shorter braking distances because they can apply more braking force to the wheels, which is especially important in emergencies.
- Improved Vehicle Control: Dual systems offer the driver more options for controlling the vehicle’s speed and stopping distance. If one system malfunctions, the other can help maintain control.
Disadvantages of a Dual Air Brake System
- Increased Complexity: Dual air brake systems are more complex than single systems, requiring more components and maintenance. This complexity can lead to higher initial costs and maintenance expenses.
- Increased Weight: Dual systems weigh more than single systems, potentially reducing the vehicle’s payload capacity.
- Higher Maintenance Requirements: Due to having more components, dual systems demand more maintenance, inspections, and upkeep, which can increase downtime and maintenance costs.
In summary, while dual-air brake systems significantly enhance safety and control, they come with the drawbacks of increased complexity, weight, and maintenance requirements. These trade-offs are considered worthwhile for their safety benefits, particularly in heavy commercial vehicles.
What is the benefit of dual circuit in brake system?
A dual-circuit brake system, often found in modern automotive braking systems, provides a crucial safety advantage by dividing the braking system into two independent circuits. Each circuit operates a subset of the vehicle’s brakes (usually front and rear axles), and if one circuit fails due to a leak or malfunction, the other remains functional.
This redundancy significantly reduces the risk of complete brake failure, enhancing safety. It allows the driver to maintain control and stop the vehicle even in a brake system failure. Dual-circuit brake systems are a fundamental safety feature, ensuring braking reliability and accident prevention on the road.
How does a dual diaphragm brake booster work?
A dual diaphragm brake booster, also known as a tandem diaphragm brake booster, is a critical component of modern automotive braking systems, designed to enhance braking efficiency and reduce the effort required by the driver to apply the brakes. Here’s how it operates:
- Vacuum Assistance: The brake booster relies on engine vacuum as a power source. The engine generates vacuum in the intake manifold during operation, creating a region of lower air pressure.
- Dual Diaphragm Design: The dual diaphragm brake booster consists of two diaphragms, typically arranged one behind the other. The front diaphragm is larger, while the rear diaphragm is smaller. A rigid center plate separates them.
- At Rest: When the driver is not applying the brakes, both diaphragms are in a neutral position, with balanced air pressure on either side of the center plate.
- Brake Pedal Activation: When the driver presses the brake pedal, it pushes a pushrod connected to the front diaphragm. This action creates an imbalance in air pressure between the front and rear diaphragms.
- Enhanced Brake Force: The incoming atmospheric air combines with the vacuum from the engine to exert additional force on the front diaphragm. This force is transmitted to the brake master cylinder.
- Assist Mechanism: The pressure differential forces the front diaphragm forward. This movement causes the front diaphragm to pull in atmospheric air from the rear side of the booster.
- Brake Actuation: The brake master cylinder pressurizes the brake fluid in the brake lines, leading to the application of force on the brake calipers or wheel cylinders. This, in turn, results in the compression of the brake pads or shoes against the brake rotors or drums, leading to vehicle deceleration or stopping.
Dual diaphragm brake boosters are favored for their improved pedal feel and responsiveness. They ensure drivers can apply the brakes with less effort, enhancing safety and driving comfort. This design is a significant advancement over earlier single diaphragm brake boosters, contributing to the effectiveness and reliability of modern braking systems.
New Brakes Making Rubbing Noise; Why?
solidcarcare.com






